Step-by-Step Guide: Setting Up Your HVAC System
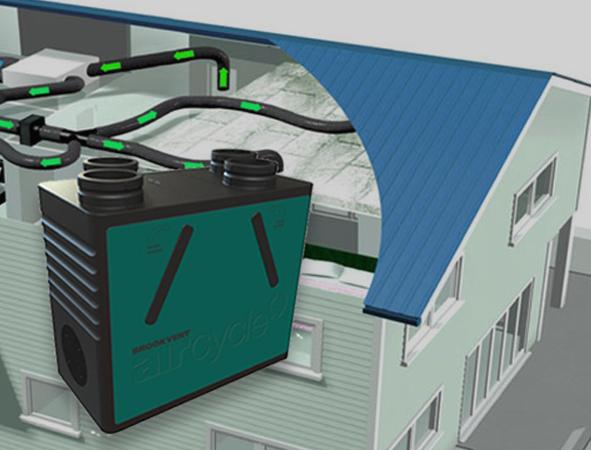
An Hvac System, short for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning, plays a crucial role in regulating indoor comfort by managing temperature, humidity, and air quality. The system typically comprises various components, including indoor and outdoor units, ductwork, and a thermostat for control. The indoor unit handles the air distribution, while the outdoor unit houses the compressor and condenser. Ductwork channels the conditioned air throughout the space, and the thermostat provides user control over the system’s functions. Correctly understanding these components and their roles is essential for effective installation and operation.
Gathering Required Tools and Materials of Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning System
Before commencing the installation, assemble all necessary tools and materials. Essential tools include a drill, screwdrivers, pliers, pipe cutter, level, and safety gear such as gloves and goggles. The materials required may differ depending on the specific Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning system type but generally consist of ductwork, electrical wiring, refrigerant lines, insulation, and HVAC units. Additionally, having access to a voltmeter and manifold gauge set can be beneficial for checking electrical connections and refrigerant levels. Ensure all tools work well to facilitate a smooth installation process.
Assessing the Space OF Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning System
Before beginning the installation, it is essential to evaluate the designated area. Measure the space to determine the appropriate system size for efficient performance. Inspect existing ductwork and electrical connections to see if they need upgrades. The location's ventilation and insulation levels should also be assessed, as these factors can impact system efficiency. Consider potential obstacles that might hinder airflow or access for maintenance. Assessing these elements will inform decisions on component placement and necessary adjustments.
Choosing the Right Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning System
Choosing the right Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning system depends on space size, local climate, and specific requirements like energy efficiency. Options include split systems, ductless mini-splits, and central systems. Evaluate the system's energy rating and ensure it is compatible with existing infrastructure for optimal performance. Consider the initial cost and long-term energy efficiency savings when selecting. Consulting with a professional can provide insights into the most suitable system for specific needs.
Installation of the Indoor Unit OF Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning system
Position the indoor unit to ensure optimal airflow and easy maintenance access. Use a level to confirm the unit is horizontally aligned. Secure it firmly with appropriate fasteners. Ensure there is sufficient clearance around the unit for efficient operation and servicing.
Connect the refrigerant lines and condense the drain according to the manufacturer's instructions to ensure no leaks. Attach the necessary electrical connections, following the specified guidelines for safety and compliance. Double-check all connections and components to ensure they are secure and properly installed.
Installing the Outdoor Unit of Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning system
Select a location for the outdoor unit that is free from obstructions and allows adequate ventilation. The unit should be placed on a stable surface to prevent vibration and noise. Secure the unit using mounting brackets or a concrete pad, and ensure it is elevated to avoid water damage.
Connect the refrigerant lines and electrical wiring according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Check for proper clearance around the unit to ensure unobstructed airflow. Insulate the refrigerant lines to maintain efficiency and prevent condensation. Verify all connections for tightness and proper sealing to prevent leaks.
Connecting Ductwork and Vents of Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning System
Connect the ductwork to the indoor unit, ensuring airtight seals to prevent energy loss and maintain system efficiency. Measure and cut duct sections accurately, then join them using appropriate connectors and sealant. Position vents throughout the space to promote even air distribution, avoiding placing them near obstacles that could obstruct airflow. Secure the ducts with brackets or straps to prevent sagging and maintain structural integrity.
Insulate the ducts, particularly those passing through unconditioned spaces, to preserve the temperature of the conditioned air. Use flexible ducting for areas where rigid ducts cannot be installed, but keep bends to a minimum to reduce resistance. Regularly inspect connections and seals for any signs of wear or leaks, addressing any issues promptly to ensure optimal performance.
Electrical Connections of Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning System
Ensure all power is turned off before beginning electrical work to avoid hazards. Identify the main electrical panel and locate the circuit breakers corresponding to the Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning system. Use the manufacturer's wiring diagram to accurately connect the HVAC unit to the power supply. Employ suitable gauge wires and connectors, adhering to local electrical codes and regulations.
Secure all connections with wire nuts and electrical tape to prevent exposed wiring. Install a disconnect switch near the HVAC units for emergency power cut-off. Double-check all connections for tightness and proper insulation. After completing the wiring, restore power and test the system to verify correct electrical operation. Use a voltmeter to ensure appropriate voltage levels and check all safety mechanisms, including fuses and circuit breakers, to confirm they function correctly.
Testing OF the Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning System
Conduct a comprehensive test of the Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning system to ensure all components function correctly. Start by setting the thermostat to cooling mode and verify that the outdoor unit activates and cool air is distributed through the vents. Observe the system's operation for any unusual noises, vibrations, or irregularities in performance. Switch the thermostat to heating mode and confirm the heating element or furnace activates and distributes warm air.
Check for any leaks in the refrigerant lines or ductwork, and ensure the condensate drain functions properly. A thermometer measures the air temperature at different vents to verify even distribution. Monitor the system for a complete cycle to maintain the set temperature. Ensure all safety mechanisms, such as circuit breakers and fuses, operate as intended. Adjust settings as needed based on the observed performance.
Adjusting System Settings About Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning System
Adjust the thermostat settings to optimise comfort and energy use. Set the thermostat to the desired temperature for different times of day, considering periods of occupancy and vacancy. Use programmable settings to automate adjustments, ensuring the system runs efficiently without manual intervention.
In cooling mode, set the thermostat slightly higher when the space is unoccupied to save energy. In heating mode, lower the temperature during unoccupied periods. Calibrate the thermostat periodically to ensure accurate readings. Consider using smart thermostats for remote access and advanced energy-saving features. These adjustments enhance comfort and contribute to reduced energy bills and prolonged system life.
Maintenance Tips about Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning System
Routine maintenance is crucial for ensuring an Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning system operates efficiently. Regularly clean or replace filters to maintain good air quality and system performance. Inspect and clean ductwork to prevent blockages and leaks that could compromise efficiency. Check refrigerant levels and top up if necessary to avoid strain on the compressor. Clean the condenser and evaporator coils to enhance heat exchange efficiency. Verify the accuracy of the thermostat and recalibrate it if required. Lubricate moving parts, such as fan motors and bearings, to minimise wear and tear. Inspect electrical connections for signs of damage or corrosion and tighten them as needed. Schedule professional maintenance at least once a year for a thorough system check-up.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning System
Common issues with HVAC-systems include poor airflow, unusual noises, and thermostat malfunctions. Inadequate airflow can result from clogged filters, obstructed ductwork, or failing blower motors. Unusual noises may indicate loose components, worn bearings, or debris in the fan.
Thermostat malfunctions might be due to incorrect settings, faulty wiring, or a need for recalibration. Inspect and clean filters regularly, check ductwork for obstructions, and ensure all electrical connections are secure. If issues persist, it is advisable to consult a professional technician for further diagnosis and repair. Prompt attention to these problems can prevent more significant damage and maintain system efficiency.
Conclusion
Correctly installing an HVAC system requires detailed planning and adherence to best practices. This ensures the system performs efficiently and has a long operational life. Understanding each component and its role, along with the meticulous execution of each installation step, can significantly enhance indoor comfort. Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are crucial for keeping the system running smoothly. Ensuring optimal placement of units, secure electrical connections, and adequate ductwork contribute significantly to overall performance. Employing energy-saving settings on the thermostat can also lead to reduced utility bills. Consulting professionals, when needed, can provide additional insights and ensure compliance with local regulations.
FAQS
Q1: How often should HVAC filters be changed?
A: Depending on usage and air quality, HVAC filters should generally be replaced every 1-3 months.
Q2: Can a Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning system be installed by oneself?
A: While those with technical skills might attempt basic installations, hiring a professional for complex systems is recommended to ensure safety and compliance with regulations.
Q3: What is the average lifespan of a HVAC system?
A: A Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning system typically lasts 15-20 years with proper maintenance.
Q4: How can the energy efficiency of a Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning system be improved?
A: Efficiency can be improved by regularly maintaining the system, using a programmable thermostat, and ensuring adequate insulation in the space.
|
Related Business Listings |





